
|
|
INDUCED GOVERNMENT PURCHASES: Government purchases that depend on income or production (especially national income or gross national product). An increase in national income triggers an increase in induced government purchases. Induced government purchases is graphically depicted as the slope of the government purchases line and is measured by the marginal propensity for government purchases. The induced relation between income and government purchases, as well as other induced expenditures, form the foundation of the multiplier effect triggered by changes in autonomous expenditures.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           AVERAGE FACTOR COST AND MARGINAL FACTOR COST: A mathematical connection between average factor cost and marginal factor cost stating that the change in the average factor cost depends on a comparison between average factor cost and marginal factor cost. For perfect competition, with no market control, marginal factor cost is equal to average factor cost, and average factor cost does not change. For monopsony and other firms with market control, marginal factor cost is greater than average factor cost, and average factor cost rises. The relation between average factor cost and marginal factor cost is one of several that reflect the general relation between a marginal and the corresponding average. The general relation is this:- If the marginal is less than the average, then the average declines.
- If the marginal is greater than the average, then the average rises.
- If the marginal is equal to the average, then the average does not change.
This general relation surfaces throughout the study of economics. It also applies to average and marginal product, average and marginal cost, average and marginal revenue',500,400)">marginal revenue, average and marginal propensity to consume, and well, any other average and marginal encountered in economics.Marginal Equals Average| Perfect Competition | 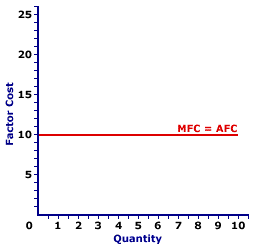 |
The equality between average factor cost and marginal factor cost occurs for a firm hiring an input in a perfectly competitive factor market. This is illustrated by the exhibit to the right. This exhibit contains the average factor cost curve and marginal factor cost curve for labor hired by Maggie's Macrame Shoppe, a hypothetical store in Shady Valley. Maggie's Macrame Shoppe is one of thousands of small retail stores in the greater Shady Valley metropolitan area that hires labor with identical skills. As such, Maggie pays the going wage for labor.The primary observation from this exhibit is that (apparently) only one curve is displayed. This single horizontal line, labeled MFC = AFC, is actually two curves, the marginal factor cost curve and the average factor cost curve. They appear to be one curve because each overlays the other. They coincide because marginal factor cost is equal to average factor cost at every input quantity. The equality between marginal factor cost and average factor cost is the result of perfect competition. Because Maggie pays the same per unit wage for every worker, incremental factor cost is equal to the per unit factor cost. Marginal Greater Than Average| Monopsony | 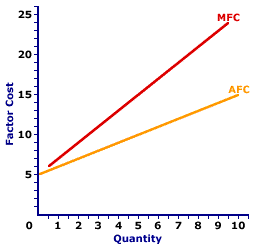 |
Marginal factor cost exceeding average factor cost occurs for a firm hiring an input in a monopsony factor market. This is illustrated by the exhibit to the right. This exhibit contains the average factor cost curve and marginal factor cost curve for labor hired by another hypothetical firm, OmniKing Island Resort. This firm is the only employer of labor on a small tropical island. As the only employer on the island, OmniKing is a monopsony with extensive market control, and it faces a positively-sloped supply curve. To employ more workers, OmniKing pays a higher price.The primary observation from this exhibit is that the positively-sloped marginal factor cost curve lies above the positively-sloped average factor cost curve. The juxtaposition of these two curves illustrates the marginal-greater-than-average aspect of the general relation. Because marginal factor cost is greater than average factor cost, the average factor cost curve increases. With market control, OmniKing faces a positively sloped factor supply curve and must pay a higher price to employ more labor. Suppose, for example, that OmniKing increases the quantity of labor hired from 5 to 6. To do so, it must increase the wage paid from $10 to $11 per worker. The average factor cost for six workers is $11, the new wage. However, the increase in the wage is paid to all workers. What happens to OmniKing's marginal factor cost when it pays a higher the wage? Two forces are at work: (1) the extra factor cost by paying the new worker and (2) the extra factor cost of the higher wage paid to other workers. Marginal factor cost is the combination of both. - First, by raising the wage, OmniKing increases the quantity employed from 5 to 6 workers. This extra worker adds an extra $11 to factor cost, the wage paid the sixth worker. This is $11 of extra cost that OmniKing did NOT incur at the lower price. If this was all to the story, then OmniKing would have a marginal factor cost of $11 for the sixth worker, equal to the wage.
- Second, by raising its price, OmniKing incurs a greater cost from its other 5 workers. Without the wage increase, it pays $10 per worker for a total of $50. But with the higher $11 price it pays $55 to these workers, an increase of total factor cost by $5, or $1 per worker.
The $11 cost incurred by hiring the extra worker is combined with the $5 additional cost paid to the other workers. Overall, total factor cost increases by only $16. The extra cost paid to existing workers is the key reason that marginal factor cost is greater than factor price and average factor cost.

Recommended Citation:AVERAGE FACTOR COST AND MARGINAL FACTOR COST, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: May 8, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GREEN LOGIGUIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time surfing the Internet looking to buy either a replacement battery for your pocket calculator or a how-to book on home remodeling. Be on the lookout for rusty deck screws.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Natural gas has no odor. The smell is added artificially so that leaks can be detected.
|

|
|
"Enthusiasm is the greatest asset in the world. It beats money and power and influence. It is no more or less than faith in action. " -- Henry Chester, Writer
|

|
OLS
Ordinary Least Squares
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


